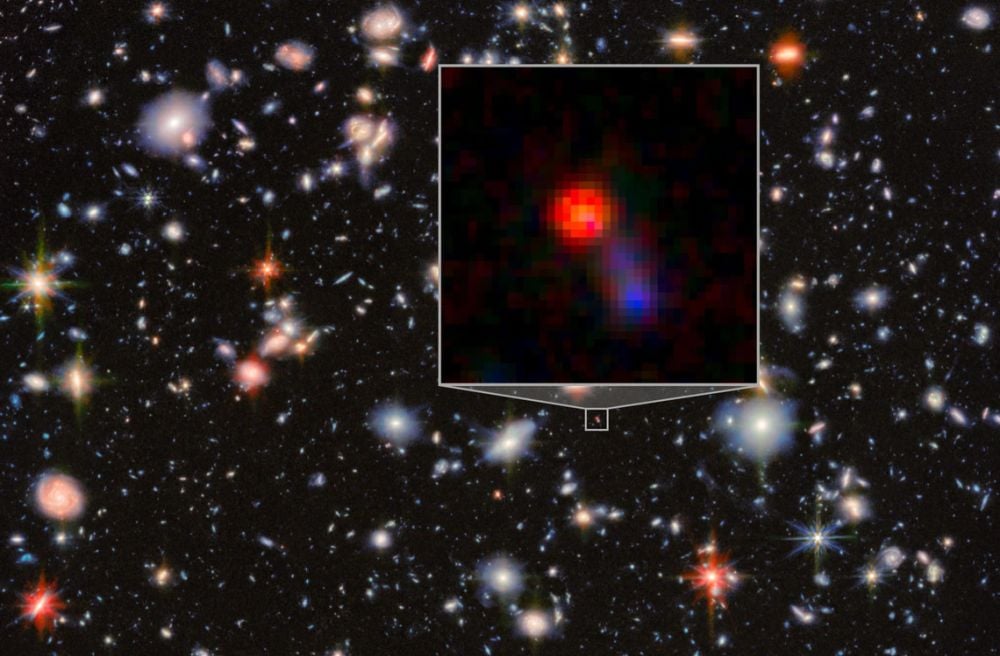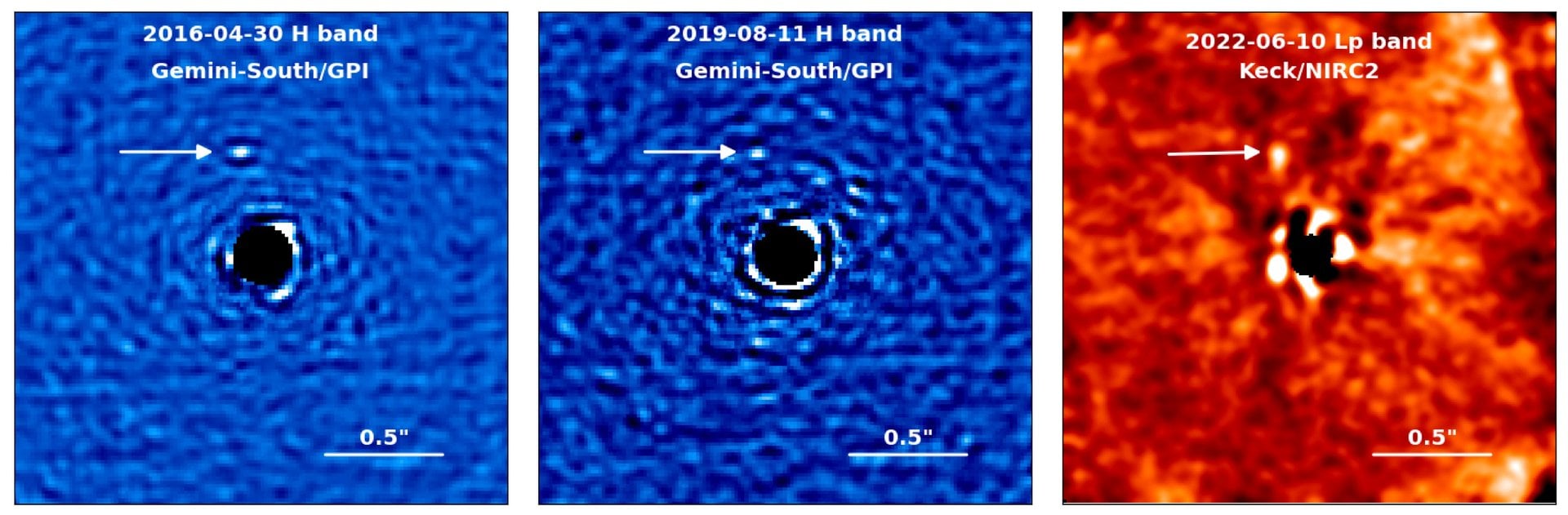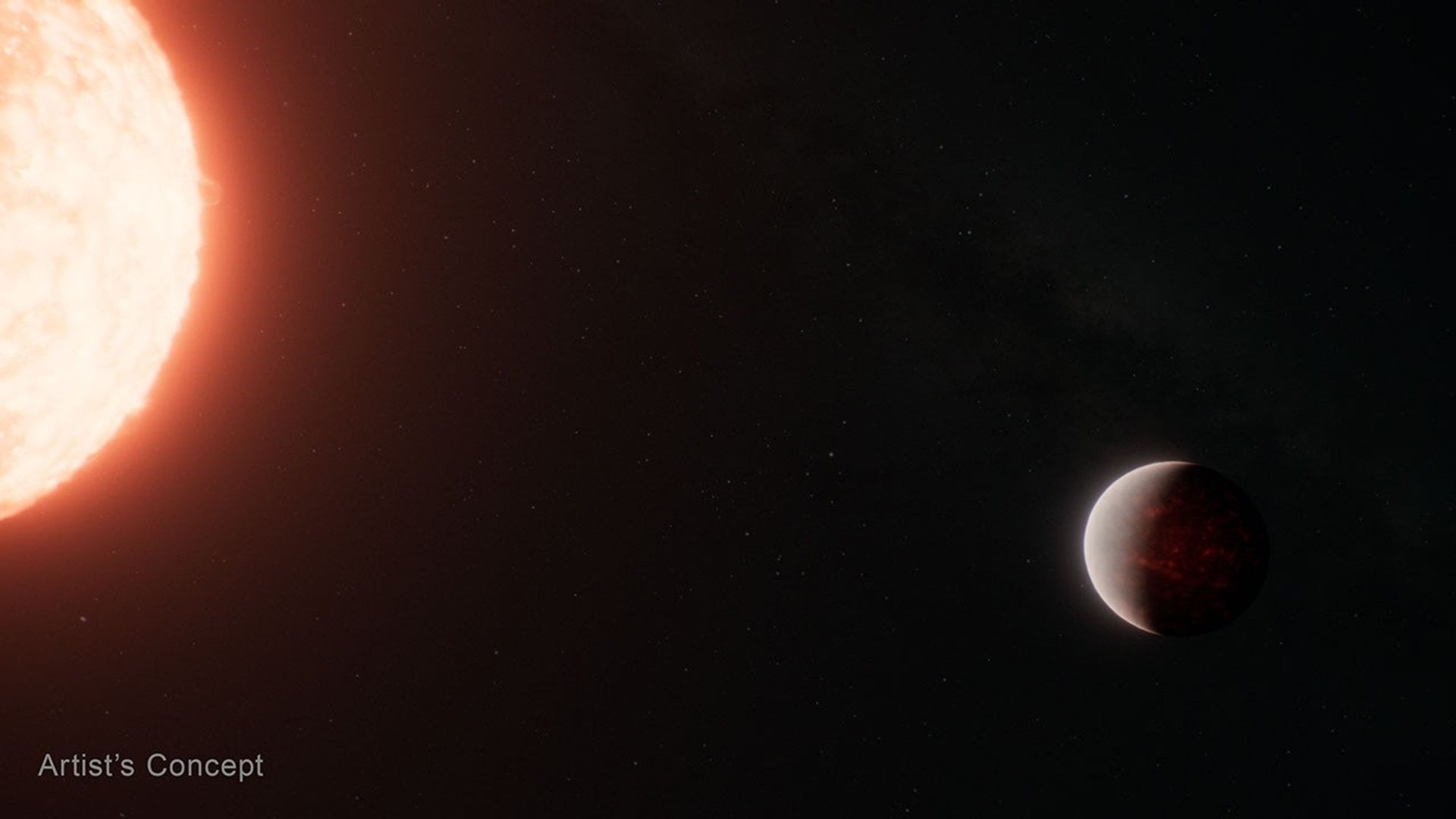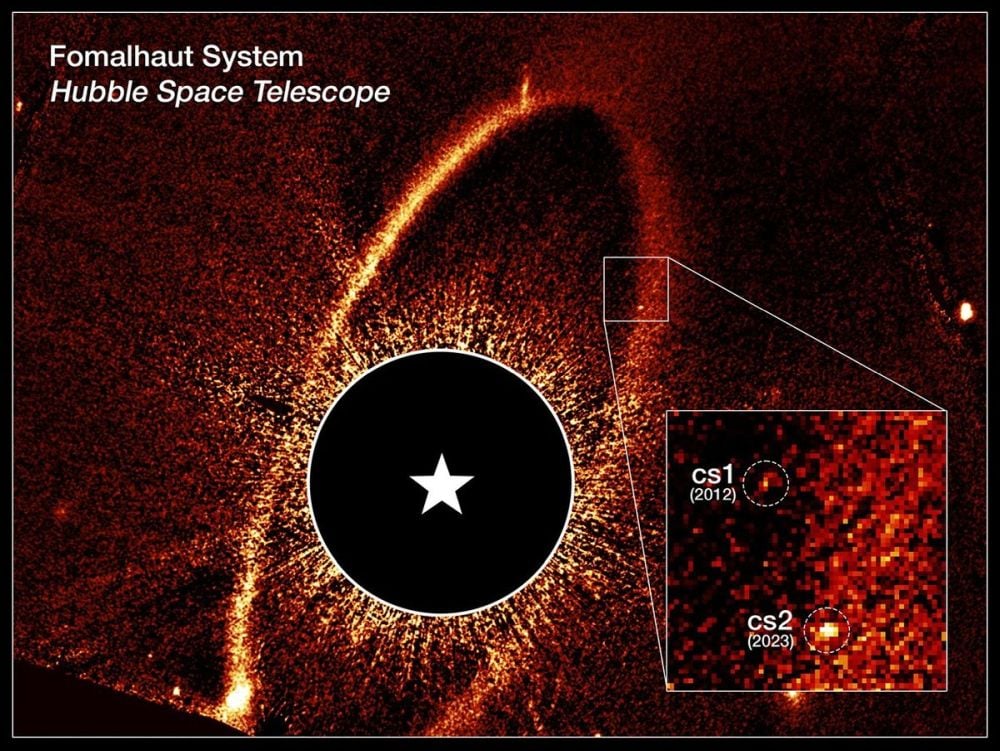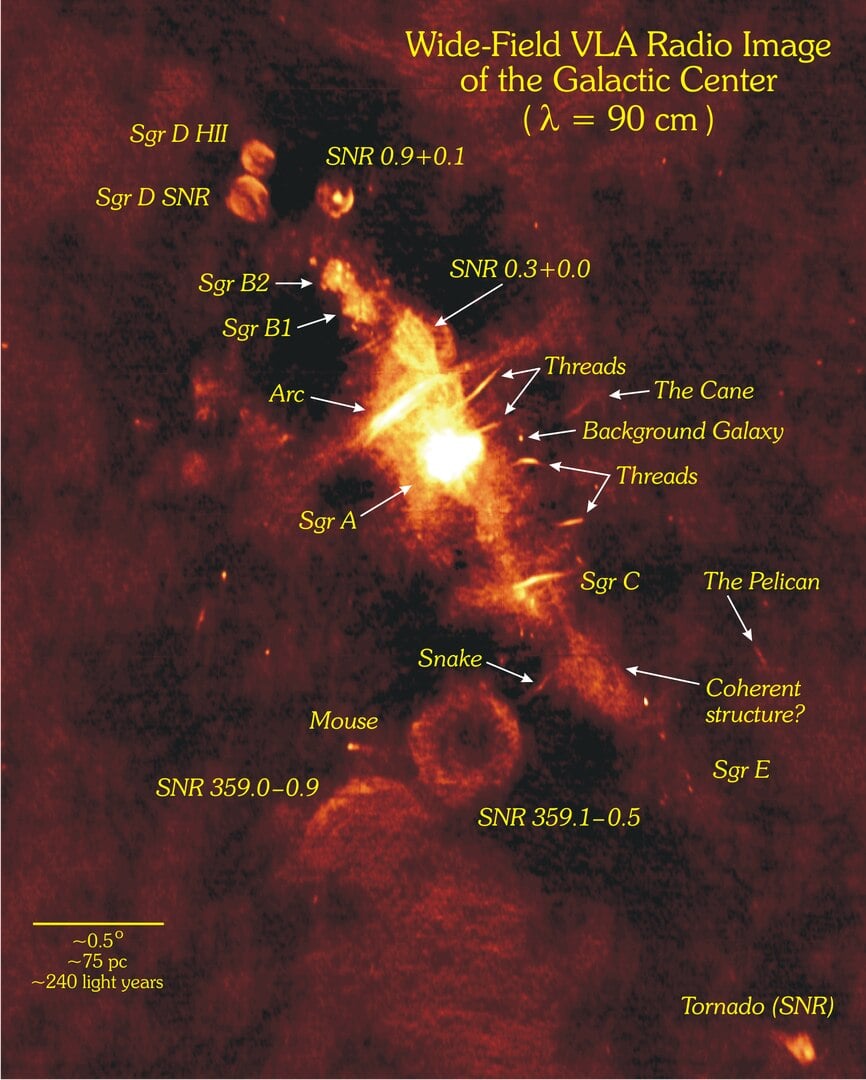
One of the primary goals of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is to detect atmospheres around exoplanets, to try to suss out whether or not they could potentially support life. But, in order to do that, scientists have to know where to look, and the exoplanet has to actually have an atmosphere. While scientists know the location of about 6000 exoplanets currently, they also believe that many of them don’t have atmospheres and that, of the ones that do, many aren’t really Earth-sized. And of those, many are around stars that are too bright for our current crop of telescopes to see their atmosphere. All those restrictions mean, ultimately, even with 6000 potential candidates, the number of Earth-sized ones that we could find an atmosphere for is relatively small. So a new paper available on arXiv from Jonathan Barrientos of Cal Tech and his co-authors that describes five new exoplanets around M-dwarf stars - two of which may have an atmosphere - is big news for astrobiologists and exoplanet hunters alike.